Tioacetal formation
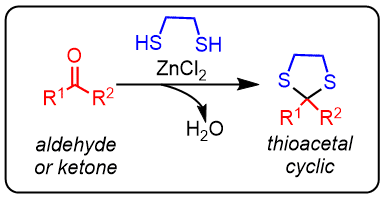
Thioacetals are obtained by heating an aldehyde or ketone with a thiol in the presence of a Lewis acid.
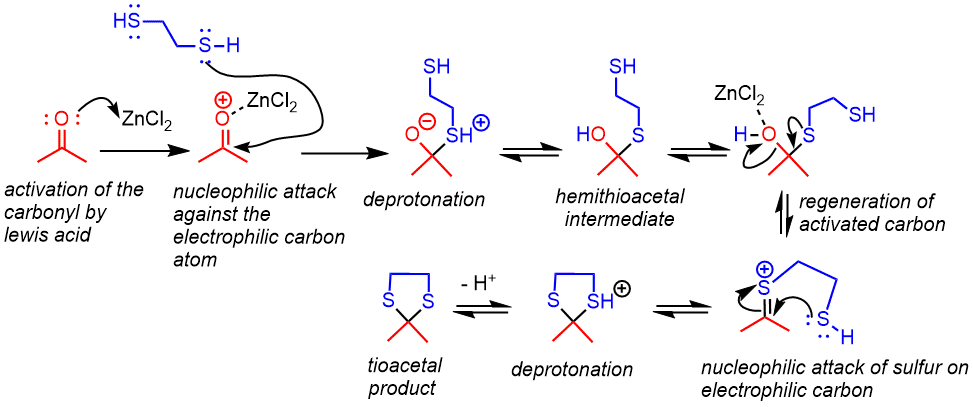
Mechanism
- The oxygen from the carbonyl gives its electron pair to the Lewis acid catalyst, activating the carbonyl.
- The nucleophilic thiol attacks the electrophilic carbon of the carbonyl, which is followed by proton transfer to produce a hemithioacetal.
- Activation of the alcohol with the Lewis acid makes it a good leaving group, and the sulfur forms a positively charged C=S species.
- Thiol attack generates the thioacetal after a final proton transfer.